 |
| NPHS 1510: Federal and International |
| Geographic Information Systems (GIS) |
|
| |
| ArcGIS |
| |
| This section will give you a quick introduction to ArcGIS. Our focus here is to provide you with the capability of using data that is ArcGIS format. |
| |
| Resources: |
| Ormsby, Tom; Napoleon, Eileen; Burke, Robert; Groessl, Carolyn; Bowden, Laura. Getting to Know ArcGIS Desktop. ESRI Press, Redlands CA, 2010. ISBN: 9781589482609. | |  |
|
|
| |
Your student version of ArcGIS came with a number of applications. We do not have the time here to teach you the intricasies of all of these very robust applications. Instead, we will focus on teaching you a tiny fraction of that which is available in a single application, ArcMap. By understanding some of the very elementary ArcMap capabilities, we hope you will get an appreciation for how GIS can be a tremendous asset to emergency decision makers.
Your full ArcGIS package includes:
- ArcCatalog - provides the necessary tools which allow you to:
- Browse and find geographic information
- Record, view, and manage metadata
- Define, export, and import geodatabase data models and datasets
- Search for and discover GIS data on local networks and the Web
- Create and manage the schemas of geodatabases
|
ArcCatalog Main Screen
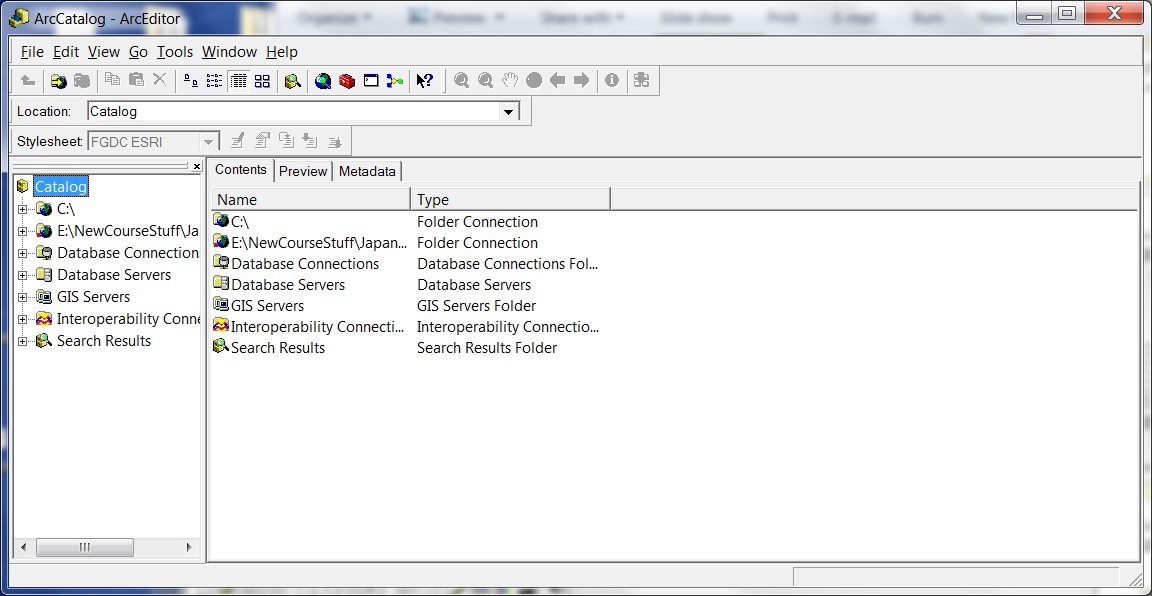 |
| |
ArcGlobe - allows users to view and analyze very large amounts of 3D GIS data seamlessly and with extremely fast display speeds. ArcGlobe literally presents a globe of the earth over which users can navigate easily in three dimensions.
ArcGlobe features include:
- Display multiresolution image and terrain data.
- Support vector data (e.g., points, lines, polygons, and 3D objects).
- Convert two-dimensional representations to 3D on the fly.
- Other features that are currently part of ArcGlobe include
- Support for identify, select, find, and text/labeling
- Animation functionality that offers a quick and easy way of creating 3D visualization (with options to export to a video format)
- Various layer effects such as transparency, lighting, shading, and depth priority
|
ArcGlobe Main Screen
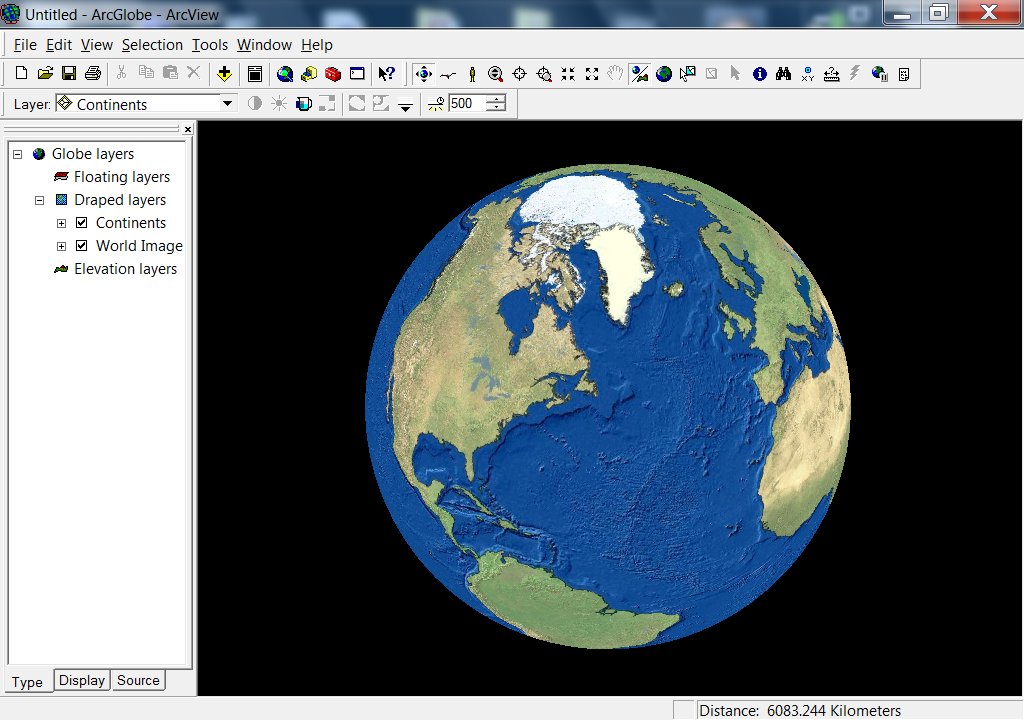 |
| |
ArcMap - an integrated desktop application that allows the user to:
- Create maps and interactive visualizations.
- Visually model and spatially analyze a process or workflow.
- Create interactive maps from file, database, and online sources.
- Create street-level maps that incorporate GPS locations.
- View CAD data or satellite images.
- Generate reports and charts.
|
ArcMap Main Screen
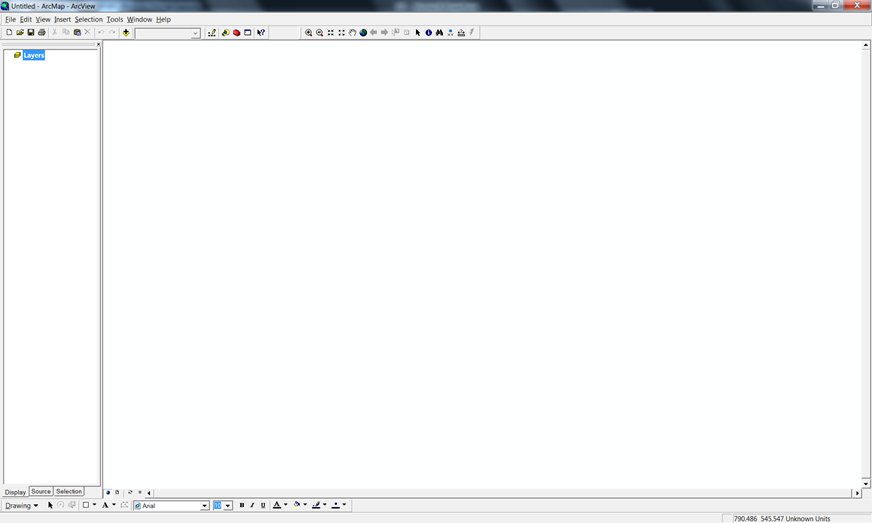 |
| |
|
ArcReader - a free, easy-to-use desktop mapping application that allows users to view, explore, and print maps and globes. Anyone with ArcReader can view high-quality interactive maps authored by a high-level ArcGIS for Desktop product and published with the ArcGIS Publisher extension.
|
ArcReader Main Screen
 |
| |
|
ArcScene - a 3D visualization application that allows you to view your GIS data in three dimensions. ArcScene allows you to overlay many layers of data in a 3D environment. Features are placed in 3D by reading height information from feature geometry, feature attributes, layer properties, or a defined 3D surface, and every layer in the 3D view can be handled differently. Data with different spatial references will be projected to a common projection, or data can be displayed using relative coordinates only. ArcScene is also fully integrated with the geoprocessing environment, providing access to many analytical tools and functions.
|
ArcScene Main Screen
 |
| |
| Exercise: |
After completing this lesson on GIS, explore some of the other applications available in ArcGIS. We spacifically reccommend that you look at ArcCatalog and ArcGlobe. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Copyright © 2011 Ken Sochats |















