 |
| NPHS 1510: Federal and International |
| Exercises |
|
| |
| Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP) |
| |
| Definition: |
Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP): A capabilities and performance-based exercise program that provides a standardized methodology and terminology for exercise design, development, conduct, evaluation, and improvement planning.
Source:
National Response Framework Resource Center
|
|
| |
| The Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP) was developed as a standard for the development of exercises for federal agencies. Each agency is required to perform a HSEEP compliant exercise each year. |
| |
| FEMA Exercise Training |
| |
|
|
| HSEEP Program and Project Management Cycle |
| |
| HSEEP is defined as a continuous programmatic cyclical activity. The diagram below shows the HSEEP Program and Project Management Cycle. The concept is that an exercise tailored to a specific need is planned. The exercise is executed. The exercise outcomes are analyzed. Corrections are made to the organization based on the results and new ideas are fed into the next planning cycle. |
| |
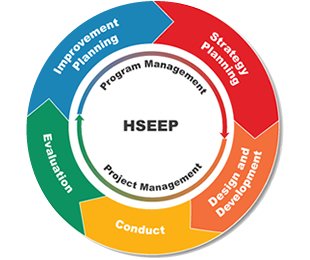 |
| |
HSEEP Program and Project Management Processes
- Managing an exercise program
- Designing and developing an exercise
- Conducting an exercise
- Evaluating an exercise
- Developing and implementing an improvement plan
|
| HSEEP Exercise Documentation |
| |
| HSEEP Documentation is provided in a five volume set. The five volumes are outlined below. Each volume is available a a download on the FEMA web site. |
| |
| HSEEP Volume I: | HSEEP Overview and Exercise Program Management provides guidance for building and maintaining an effective exercise program and summarizes the planning and evaluation process described in further detail in Volumes II through V.
|
| HSEEP Volume II: | Exercise Planning and Conduct helps planners outline a standardized foundation, design, development, and conduct process adaptable to any type of exercise.
|
| HSEEP Volume III: | Exercise Evaluation and Improvement Planning offers proven methodology for evaluating and documenting exercises and implementing an improvement plan.
|
| HSEEP Volume IV: | Sample Exercise Documents and Formats provides sample exercise materials referenced in HSEEP Volumes I, II, III, and V.
|
| HSEEP Volume V: | Prevention Exercises contains guidance consistent with the HSEEP model to assist jurisdictions in designing and evaluating exercises that test pre-incident capabilities such as intelligence analysis and information sharing.
|
|
| |
| Types of Exercises |
| |
| HSEEP exercises are classified according to the involvement and resources required for the exercise type. The exercise types are: |
| |
| Discussion-based Exercises |
Familiarize participants with current plans, policies, agreements, and procedures, or may be used to develop new plans, policies, agreements, and procedures. |
| Operations-based Exercises |
Validate plans, policies, agreements and procedures; clarify roles and responsibilities; and identify resource gaps in an operational environment.
|
|
| |
| Discussion Exercises |
| |
| Seminar | A seminar is an informal discussion, designed to orient participants to new or updated plans, policies, or procedures (e.g., a seminar to review a new Evacuation Standard Operating Procedure).
|
| Workshop | A workshop resembles a seminar but is employed to build specific products, such as a draft plan or policy (e.g., a Training and Exercise Plan Workshop is used to develop a Multi-Year Training and Exercise Plan).
|
| Tabletop Exercise (TTX) | A tabletop exercise involves key personnel discussing simulated scenarios in an informal setting. TTXs can be used to assess plans, policies, and procedures.
|
| Games | A game is a simulation of operations that often involves two or more teams, usually in a competitive environment, using rules, data, and procedure designed to depict an actual or assumed real-life situation.
|
|
| |
| Operational Exercises |
| |
| Drill | A drill is a coordinated, supervised activity usually employed to test a single specific operation or function within a single entity (e.g., a fire department conducts a decontamination drill). |
| Functional Exercise (FE) | A functional exercise examines and/or validates the coordination, command, and control between various multi-agency coordination centers (e.g., emergency operation center, joint field office, etc.). A functional exercise does not involve any "boots on the ground" (i.e., first responders or emergency officials responding to an incident in real time). |
| Full-Scale Exercises (FSE) | A full-scale exercise is a multi-agency, multi-jurisdictional, multi-discipline exercise involving functional (e.g., joint field office, emergency operation centers, etc.) and "boots on the ground" response (e.g., firefighters decontaminating mock victims). |
|
| |
| Exercise Documents |
| |
| Each HSEEP exercise employs a number of standard documents that are developed and refined over time. The completed docuemnts serve as documentation for the exercise and the basis for exercise evaluation. The documents are detailed below: |
| |
| A Situation Manual (SitMan) | is a participant handbook for discussion-based exercises, particularly TTXs. It provides background information on exercise scope, schedule, and objectives. It also presents the scenario narrative that will drive participant discussions during the exercise. |
| The Exercise Plan (ExPlan) | typically used for operations-based exercises, provides a synopsis of the exercise and is published and distributed to players and observers prior to the start of the exercise. The ExPlan includes the exercise objectives and scope, safety procedures, and logistical considerations such as an exercise schedule. The ExPlan does not contain detailed scenario information.
|
| The Controller and Evaluator (C/E) Handbook | supplements the ExPlan for operations-based exercises, containing more detailed information about the exercise scenario and describing exercise controllers' and evaluators' roles and responsibilities. Because the C/E Handbook contains information on the scenario and exercise administration, it is distributed only to those individuals specifically designated as controllers or evaluators.
|
| The Master Scenario Events List (MSEL) | is a chronological timeline of expected actions and scripted events (i.e., injects) to be inserted into operations-based exercise play by controllers in order to generate or prompt player activity. It ensures necessary events happen so that all exercise objectives are met.
|
| A Player Handout | is a 1-2 page document usually handed out the morning of an exercise which provides a quick reference for exercise players on safety procedures, logistical considerations, exercise schedule, and other key factors and information.
|
| Exercise Evaluation Guides (EEGs) | help evaluators collect and interpret relevant exercise observations. EEGs provide evaluators with information on what tasks they should expect to see accomplished during an exercise, space to record observations, and questions to address after the exercise as a first step in the analysis process. In order to assist entities in exercise evaluation, standardized EEGs have been created that reflect capabilities-based planning tools, such as the Target Capabilities List (TCL) and the Universal Task List (UTL). The EEGs are not meant as report cards. Rather, they are intended to guide an evaluator's observations so that the evaluator focuses on capabilities and tasks relevant to exercise objectives to support development of the After Action Report/Improvement Plan (AAR/IP).
|
| An After Action Report/Improvement Plan (AAR/IP) | is the final product of an exercise. The AAR/IP has two components: an AAR, which captures observations and recommendations based on the exercise objectives as associated with the capabilities and tasks and an IP, which identifies specific corrective actions, assigns them to responsible parties, and establishes targets for their completion. The lead evaluator and the exercise planning team draft the AAR and submit it to conference participants prior to an After Action Conference (see below). The draft AAR is distributed to conference participants for review no more than 30 days after exercise conduct. The final AAR/IP is an outcome of the After Action Conference and should be disseminated to participants no more than 60 days after exercise conduct. |
|
| |
HSEEP Exercise Meetings
A HSEEP exercise is planned, conducted and analyzed over time by the exercise team. Team meetings are used to refine the exercise. The standaard meetings are given below:
- Concepts and Objectives Meeting
- Initial Planning Conference (IPC)
- Mid-Term Planning Conference (MPC)
- Master Scenario Events List (MSEL) Conference
- Final Planning Conference (FPC)
- After Action Conference (AAC)
|
| |
| HSEEP Exercise Tools |
| |
| FEMA provides a number of tools to help ageencies and organizations to manage exercise programs and conduct exercises. Some of these tools are: |
| |
| National Exercise Schedule (NEXS) System | the Nation's online comprehensive tool that facilitates scheduling, deconfliction, and synchronization of all National-Level, Federal, State, and local exercises. HSEEP User Guide: Login and Create an Exercise . HSEEP User Guide: NEXS . |
| Design and Development System (DDS) | a project management tool and comprehensive tutorial for the design, development, conduct, and evaluation of exercises. The DDS provides users with the appropriate templates and guidance from the HSEEP Volumes for developing timelines, planning teams, and exercise documentation (e.g., Situation Manuals, Exercise Plans, exercise planning conference materials). The DDS is the technological backbone for the planning process described in HSEEP Volume II: Exercise Planning and Conduct. HSEEP User Guide: DDS . |
| The Exercise Evaluation Guide (EEG) Builder | allows users to create customized EEGs both inside the Toolkit and through the website by selecting which Activities from a given Capability will be evaluated during an exercise. Users will also be able to create customized Tasks and Measures to further focus the evaluation process. HSEEP User Guide: EEG Builder . HSEEP User Guide: EEG Builder Standalone. |
| The Master Scenario Events List (MSEL) Builder | allows exercise Lead Planners to create customized MSEL formats by selecting from a list of data fields. Once a Lead Planner has created their MSEL they populate data fields with exercise specific information. Data field population allows users to select from predefined exercise information to create individual injects for a MSEL. HSEEP User Guide: MSEL Builder for MSEL Managers . HSEEP User Guide: MSEL Builder for MSEL Users . |
| Corrective Action Program (CAP) System | a web-based application that enables users to prioritize, track, and analyze improvement plans developed from exercises and real-world events. Features of the CAP System include Improvement Plan creation and maintenance, corrective action assignment and tracking, and reporting and analysis. The CAP System functionality is based on the process described in HSEEP Volume III: Exercise Evaluation and Improvement Planning. The CAP System supports the process by which exercise and real-world events can inform and improve exercise programs and other preparedness components. CAP System FAQ. |
| HSEEP Data Exchange Standards | This website is provided by FEMA and the National Exercise Division (NED) to promote the data exchange standard for the Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP). In an effort to assist all HSEEP stakeholders with understanding and using the HSEEP Data Exchange Standards, NED has compiled relevant and useful resources and material about the HSEEP Data Exchange Standards into this one central repository. |
|
| |
| Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP) |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Copyright © 2011 Ken Sochats |










