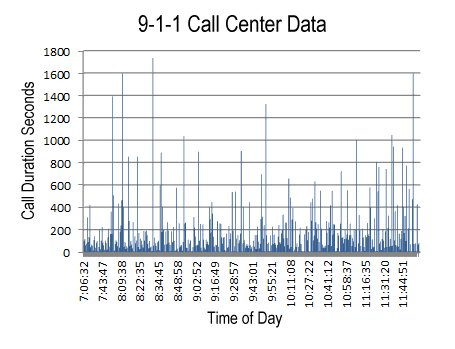
| Pittsburgh Average Daily High and Low Temperatures (2010) |
|---|
| Month | Average High
Temperature | Average Low
Temperature |
|---|
| January | 31.9 | 19.8 |
| February | 32.8 | 19.9 |
| March | 53.7 | 32.9 |
| April | 67.7 | 43 |
| May | 74.5 | 52.6 |
| June | 79.7 | 61.9 |
| July | 85.9 | 65.2 |
| August | 84.9 | 63.9 |
| September | 76.3 | 55.1 |
| October | 63.6 | 43.2 |
| November | 52.4 | 32.1 |
| December | 30.8 | 20.4 |
|
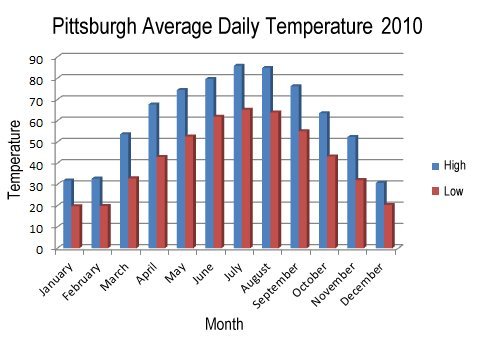 |
| Pittsburgh Monthly Rainfall (2010) |
|---|
| Month | Rainfall
Inches |
|---|
| January | 2.9 |
| February | 3.22 |
| March | 2.19 |
| April | 1.76 |
| May | 5.19 |
| June | 5.13 |
| July | 2.86 |
| August | 1.68 |
| September | 3.27 |
| October | 2.12 |
| November | 5.97 |
| December | 1.56 |
|
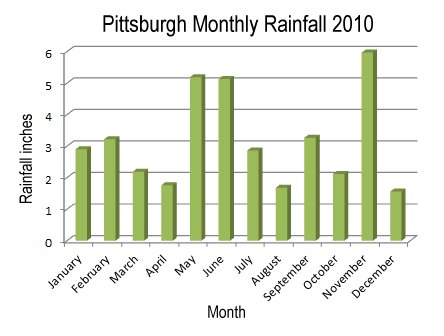 |
| US Average Births per Day (1995-2002) |
|---|
| Month | Average
Births |
|---|
| January | 10,411 |
| February | 10,662 |
| March | 10,667 |
| April | 10,574 |
| May | 10,782 |
| June | 10,956 |
| July | 11,245 |
| August | 11,345 |
| September | 11,420 |
| October | 10,865 |
| November | 10,551 |
| December | 10,611 |
|
 |
| US Average Deaths per Day (1995-2002) |
|---|
| Month | Average
Deaths |
|---|
| January | 7,357 |
| February | 7,082 |
| March | 6,831 |
| April | 6,472 |
| May | 6,229 |
| June | 6,091 |
| July | 6,030 |
| August | 5,967 |
| September | 6,051 |
| October | 6,306 |
| November | 6,502 |
| December | 6,976 |
|
 |
|