 |
| Data |
| |
|
  


|
    
|
|
| |
| Data |
| We can define data as the evidence that a system is functioning. Collecting data is one of the most important functions of an emergency system.
|
| |
| Selected Reports
|
| |
| Purposes |
- Reporting
- Analysis
- Question Answering
- Modeling
- Intervention and Experimentation
|
Data and the Emergency Cycle
- Prepare
- Respond
- Recover
- Mitigate
|
| Data Formats |
- Text
- Free Text - Papers, Reports
- Structured Text
- Attribute - Value Pairs (Age - 27, SSN - 123-45-6789)
- Photographic
- Audio - 9-1-1 Calls
- Video - Surveillance Cameras
- Mixed - Reports, SARs
- Multiple
|
| Text Treatment |
- Abstract/Brief/Item/Summary
- Index
- Keywords - Aboutness
|
Data Hierarchy
- Signal - A unit of energy (electricity, sound, light, etc.) that is used to encode data.
- Data - A pattern of signals that represents something.
- Information - Interpreted or understood data.
- Knowledge - Models that can be used to process data into information.
- Wisdom - The capacity to create models.
|
| |
Signals
This section discusses signals. Understanding the fundamentals of signals is important for Emergency Management and
Homeland Security professionals. Signal detection and processing is essential for everything from detecting and
responding to emergencies and to alerting responders and potential victims. Signals are also mechanisms for carrying
information. We will examine the role that signals play in crime, terrorism and other activities.
Every activity, whether natural or man-made involves energy. Energy is present everywhere and at all times except at
absolute zero (-273 K). Energy can take the form:
- Heat
- Light
- Electrical
- Electromagnetic
- Chemical
- Radiation
- Kinetic
- Sound
|
| |
| Signals have two major uses in homeland security and national preparedness.
First, we sense or detect signals in the environment to provide us input for situation awareness. Second, we use signals
for alerting and communicating. In both cases advances in electronic technology have presented the emergency manager
with a plethora of options for use. |
| |
Note also that the use of animals has been used for a long time including:
- Canaries to detect explosive and poisonous gases in mines
- Guard dogs
- Drug sniffing animals
- Bomb decting dogs
- Other sensitive animals
|
| |
There are a wide range of signal detectors in use today. Some of these have been around for a long time, while
otheres have heen developed quite recently. The table below provides a quick overview of example simple electric deteectors in use
today.
|

Thermostat |

Smoke Detector |

Carbon Monoxide Detector |
| |

Motion Detector |

Radiation Detector |

Radon Detector |
|
| |
| More and more sophisticated detectors are being developed for emergency management. For example, police and fire use thermal imageing
detectors to determine whether perpetrators are in a building or fire is present behind a wall or door. |
| |
 |
| |
The image below gives the waveform of a gunshot. The sound if from a .40 Smith and Wesson being fired out of a subcompact Glock 27.
See: http://soundbible.com/ Recorded by Mike Koenig.
Click on the image to listen to the sound.
The City of Pittsburgh recenly installed the ShotSpotter system to detect and locate gnshot activity.
See www.shotspotter.com.
|
| |
 |
| |
| Signals are used for alerting and informing citizens. Many of the detectors above produce sounds and or lights to
gain the attention of users. Perhaps the simplest example of this is the traffic signal. |
| |
 |
| |
| Another wlwmwntary example is the system of sounds used to signal various conditions on a computer. Each sound has a frequency
or pattern that is associated with a certain condition or status. |
| |
Sampling of Windows sounds:
- Balloon
- Battery Critical
- Battery Low
- Critical Stop
- Default
- Ding
- Error
- Exclamation
- Feed Discovered
- Hardware Fail
- Hardware Insert
- Hardware Remove
- Information Bar
- Logoff
- Logon
- Navigation Start
- Notify
- Pop-up Blocked
- Print Complete
- User Account Control
|
| |
| A tornado siren uses a wailing sound to alert citizens to seek shelter. |
 |
| |
One might define a disaster as the presence of a destructive amount of energy.
Natural disasters involve the creation and/or movement of energy. The table below illustrates some examples of types of natural disasters and the types of energy involved.
|
| |
| Natural Disaster | | Forms of Energy |
| Wildfire | | Heat, Light, Chemical, Sound, Kinetic |
| Earthquake | | Sound, Kinetic |
| Thunderstorm | | Electrical, Electromagnetic, Light, Sound, Kinetic |
| Volcano | | Heat, Light, Chemical, Sound, Kinetic |
| Hurricane | | Sound, Kinetic |
|
| |
|
Man-made events can be viewed in the same manner. Consider the Department of Homeland Security's classification of events CBRNE-Cyber, Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, Explosive and Cyber. Each of these involves some form of energy. Non-intentional events such as accidents also involve energy creation/transformation.
|
| |
| Definition: |
Signal: The physical representation of a logical value.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
| We can consider a signal to be a representation of energy. We use signals to detect and characterize all of the disasters listed above as well as any other activity. Every animal, plant and many devices have the ability to sense signals. We refer to devices that have the ability to detect signals as detectors or sensors. These devices are very common. A home might have smoke detectors, carbon monoxide detectors, radiation detectors and motion detectors. Theere are litterally thousands and thousands of types of detectors available. We should also consider radios, televisions, cell phones and other devices as detectors. |
| |
| Definition: |
Noise: Unwanted disturbances superimposed on a useful signal that tend to obscure the signal's information content.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
| Signals are present everywhere at all times. Stop now and listen. How many minute things can you hear? We are really being bombarded with sounds at all times. Very few of these signals are of use to us. |
| |
Types of noise:
- Thermal, sometimes referred to as white or Gaussian
- Impulse
- Crosstalk
- Intermodulation
|
| |
| Definition: |
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR):
The ratio of signal power to noise power within a specified bandwidth, usually expressed in decibels.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio is a very important concept for us. Have you ever tried to carry on a conversation in a crowded bar? Sometimes it is impossible. We would, of course, want our sensors and detectors to respond to the intended signals and not to noise. |
| |
Examples of Signal to noise issues:
- Google searches
- Crowd surveillance
|
| |
| Definition: |
Bandwidth:
The range of frequencies within which performance, with respect to some characteristic, falls within specific limits.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
| Every animal, plant and device has a limited detection bandwidth. Normal healthy humans, for example, can hear only in the range of 20 - 20,000 cycles per second (Hertz). These devices and living things also have a limited bandwidth with the respect to the signals they create. |
| |
| Detectors have two characteristics which define their efficiency and effectiveness: sensitivity and selectivity. |
| |
| Definition: |
Sensitivity:
Sensitivity is the minimum input signal required to produce an output signal or indication that satisfies a specified requirement.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
Animals have long been known to posess sensitivities that can be useful in Emergency Management and Homeland Security.
Examples include:
- Canaries to detect poisonous gasses in mines.
- Guard dogs.
- Drug sniffing dogs.
- Search and Rescue dogs.
- Bomb Dogs.
|
| |
| Definition: |
Selectivity:
The ability or a measure of the ability of a receiver to discriminate between a given wanted signal and unwanted signals.
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
| Definition: |
Filter:
A (device) that selects or rejects one or more components of a signal...
Source: IEEE Standards Definition Database http://dictionary.ieee.org. |
|
| |
Types of filters:
- High Pass
- Low Pass
- Band Pass
- Band Stop
|
| |
| Shannon's Law
|
| C = B log2 (1 + SNR) |
Where:
C = Capacity of the Channel
B = Bandwidth
SNR = Signal to Noise Ratio
|
| |
Data Collection
| Population | Sample |
| Domain | Observations on a Population |
- Description
- Distribution
- Mean
- Median
- Mode
|
- Description
- Distribution
- Mean
- Median
- Mode
|
|
Data Collection
- Regular/Periodic
- One Time/Ad Hoc
|
| |
| Record Keeping Systems |
| |
- Administrator - Control
- Records - Definitions - Rules
- Systems - Regularity
|
| |
Recordkeeping Systems
- System Operation
- Evidence
- Used to create or validate hypotheses
- Legal
- System Design, Redesign, Recovery
Debugging
|
Recordkeeping Requirements
- CONSCIENTIOUS ORGANIZATION
-
ACCOUNTABLE RECORDKEEPING SYSTEM
2. Responsible
3. Implemented
4. Consistent
- CAPTURED RECORDS
5. Comprehensive
6. Identifiable
7. Complete
7a. Accurate
7b. Understandable
7c. Meaningful
8.Authorized
- MAINTAINED RECORDS
9. Preserved
9a. Inviolate
9b.Coherent
9c.Auditable
10. Removable
- USABLE RECORDS
11. Exportable
12. Accessible
12a. Available
12b. Renderable
12c. Evidential
13. Redactable
See Bearman and Sochats: Metadata Requirements for Evidence
|
Data Sets
- Observations of a system.
- Records
- Significant events
- Triggered (e.g. Accident Reports)
- Time oriented (e.g. Census)
- Attributes
- Regularly measured (NOIR)
- Nominal - By name
- Ordinal - Ordered on a scale
- Interval - Equal distance between scale items.
- Ratio
- Type/Format/Coding
- Domain
- Range
- Key
- Related sets – Super-, sub-, other
|
| Data Set Concepts |
| |
- Mutual Exclusivity
- Collective Exhaustiveness
- Granularity
- Raw Data - Instances
- Aggregate Data
- Statistics
- Indexes
|
| |
Data Problems
- Incomplete or missing data
- Uncollected data
- Incompatible data
- Erroneous data
- Miscoded data
A successful hoax is high quality data that is plausible.
|
| |
| Granularity |
| |
- Time
- Instant
- Time Period
- Time of Day
- Day of Week
- Holidays
- Events
- Geography
- Locality
- County
- Region
- State
- National
- Jurisdiction
|
| |
| Data Manipulation |
| |
- Search
- Aggregation
- Merge/Split
- Statistics
- Formulas
|
| |
| Data Management Systems |
| |
- Browser - Excel
- Database Management System - Access
|
| |
| Process |
| |
- Face Validity Assessment
- Feel for the Data
- Sense Making
- Context
|
Data Analysis
Assess the source
Assess the data model and system
- Collection
- Automatic – Sensors, clocks, timers, counters, etc.
- Trained Observer – Surveyors, Analysts, Investigators, etc.
- Witness
- Coding – Grouping, sorting, etc.
- Recording
- Test the data – single to multiple attribute
- Descriptive statistics
- Visual techniques – Graphs, charts, visualization
- Hypotheses
- Modeling
|
- Face Validity Assessment
- Feel for the Data
- Sense Making
- Context
|
| |
Example: 9-1-1 Call Center Data
- All calls - 31,374
- Three shifts – 6-12:00, 12-18:00, 18-24:00
- Complete call data
- January 1999
- See accompanying spreadsheet – CallCenterData.xls
|
| |
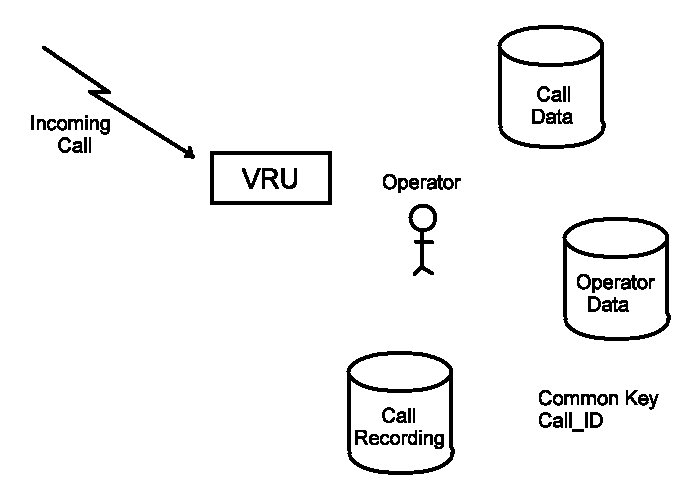
Call Center System |
| |
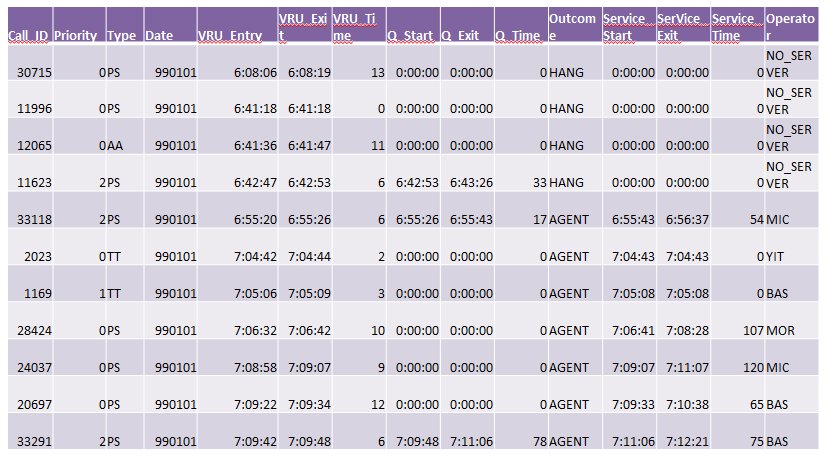
Call Center Data |
| |
Select Attributes
Unique Key – used to distinguish this record from all others (de jure)
Ordinal
Integer
Range 0+
Auto-generated
Note: The combination of Date, VRU_Entry and Operator is a Compound Key (de facto)
Priority
- Nominal
- Coded
- 0 – Non-dispatch
- 1 – Minor Event (e.g. traffic accident)
- 2 – Significant Event (e.g. fire, hazmat)
- 3 – Catastrophic Event
- Date
- Ordinal
- Integer
- Coded
- YYMMDD
- Operator
- How is this attribute coded/standardized?
- Service Time
- How is this attribute measured?
- Other Attributes?
|
System Assessment
- How should the system behave (i.e. design)
- How does the system actually behave (i.e. measurements)
- Why do these agree or not agree?
|
Data Analysis
- Microsoft Excel
- Transaction orientation (rows = records, columns = attributes)
- Mathematical operators – formulae, operators
- Relational Operators - Select, Join, Transpose
- Sorting
- Formatting
- Macros
- Cut, Copy, Paste
- Grouping
- Charts, Graphs
- See references for tutorials
|
| |
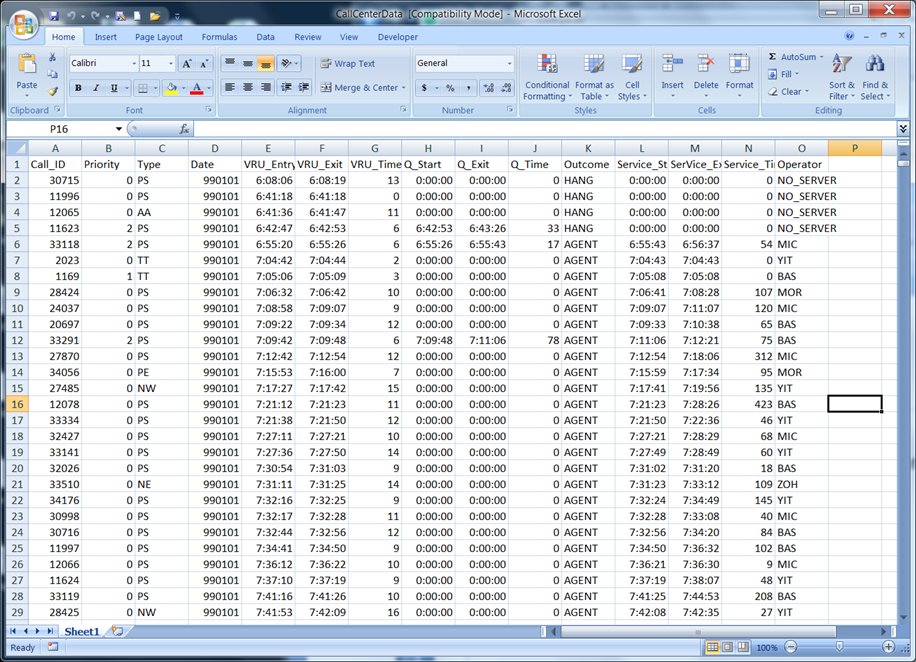
Call Center Excel Data |
| |
Single Attribute Analysis
- Descriptive
- Nominal
- Ordinal, Interval, Ratio
- Mean
- Median
- Mode
- Distribution
- Variance
|
| |
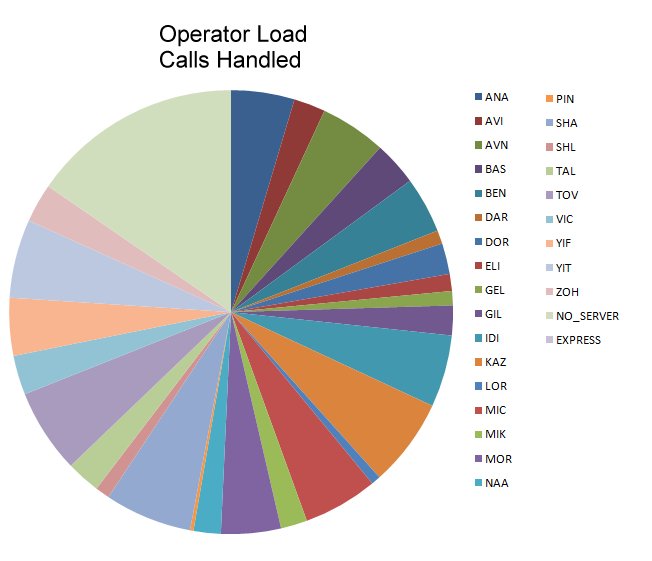
Call Center Operator Load |
| |
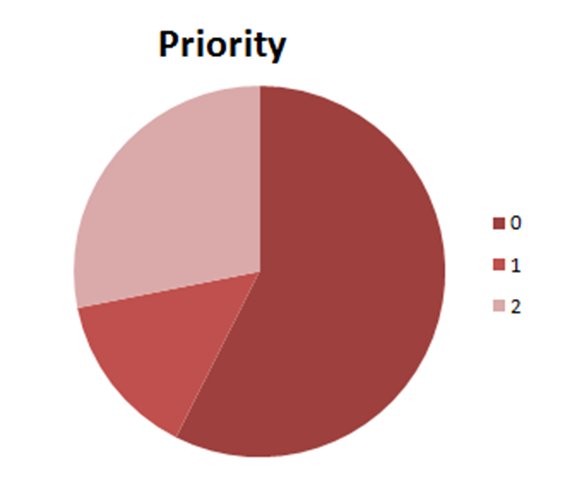
Call Center Call Priority |
| |
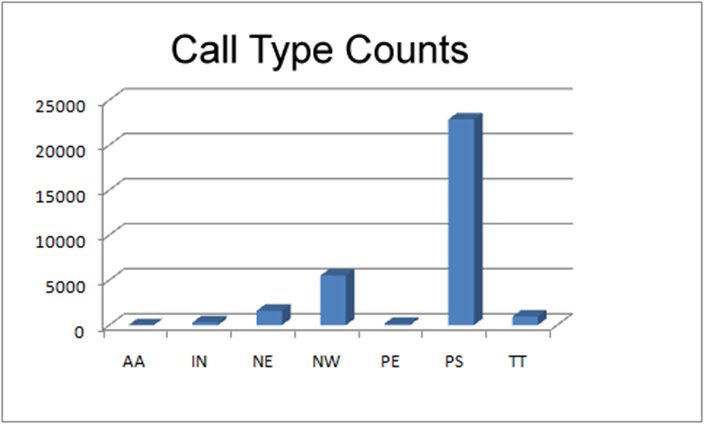
Call Center Call Types |
| |
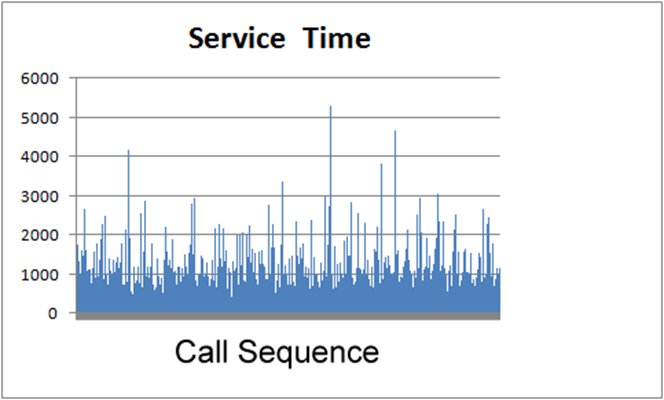
Call Center Call Durations by Sequence |
| |
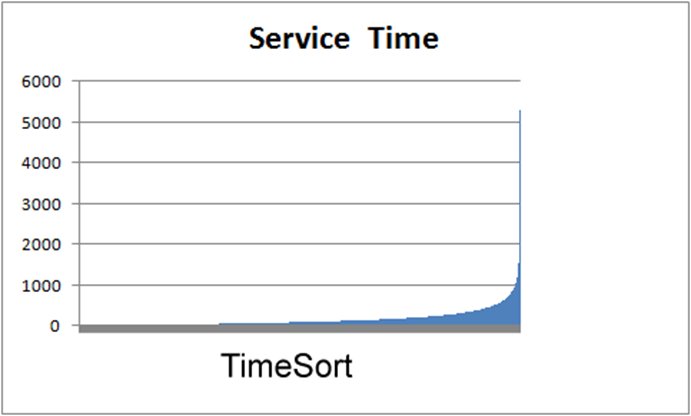
Call Center Call Durations Sorted |
| |
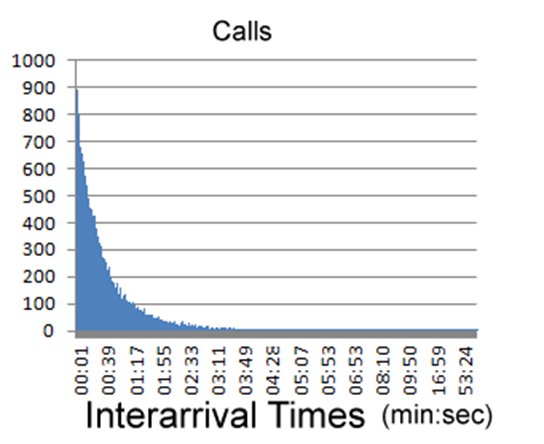
Call Center Call Interarrival Times |
| |
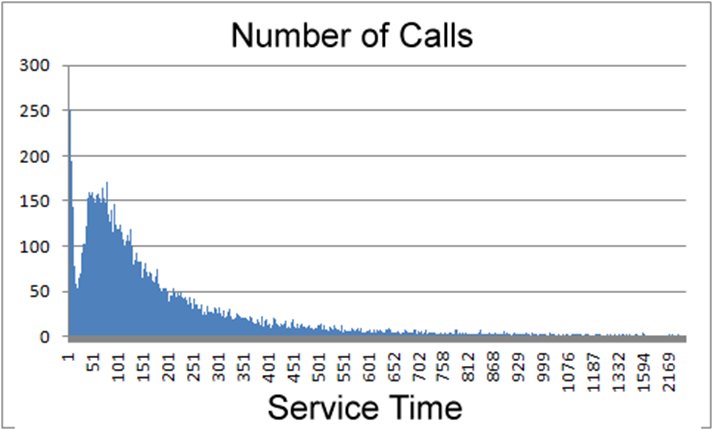
Call Center Service Time Distribution |
| |
| Multiple Attribute Analyses
|
| |
| |
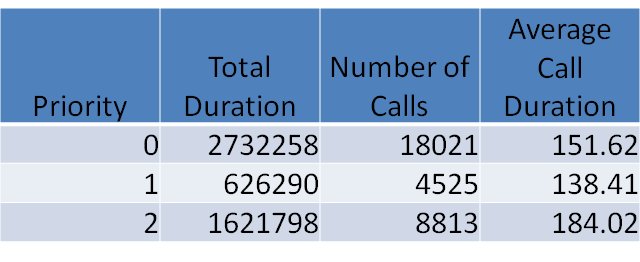
Call Center Call Duration by Priority |
| |
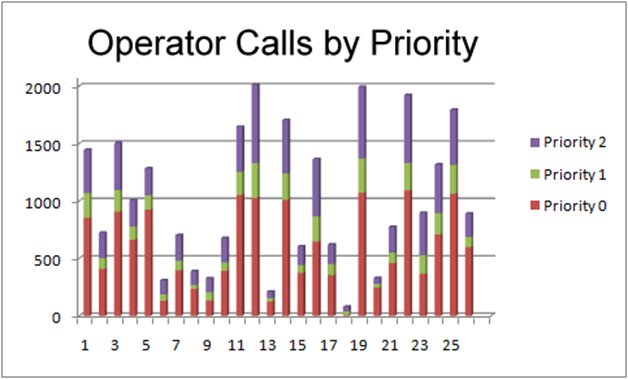
Call Center Operator Load by Priority |
| |
Further Analysis
- Year & Multiyear data
- Trends
- Aggregation
- Other System Data
- Operator Response
|
| |
| Example: South Florida Weather
|
| |
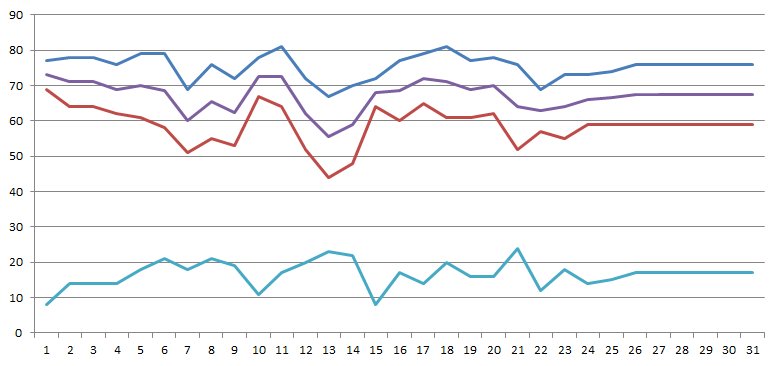
Florida January Temperatures |
| |
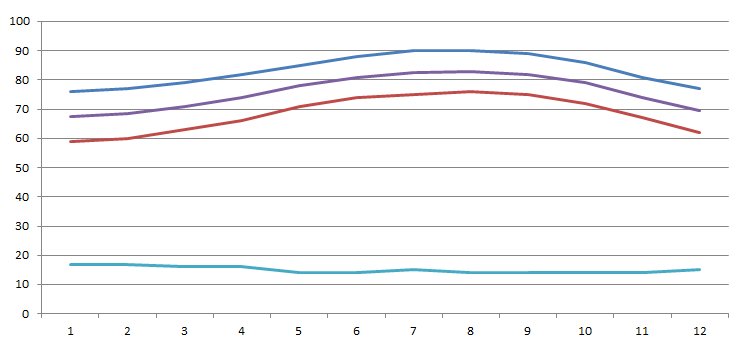
Florida Annual Temperatures |
| |
| Example: Allegheny County Arrest Records |
| |
- 2013 Year-to-Date
- Geographic/Jurisdiction
- Aggregation
- Age, Sex, Race
|
| |
| |
| Allegheny County Arrest Data |
| |
| Crime/Incident Reporting |
| |
- FBI
- Uniform Crime Report (UCR)
- Supplemental Homicide Report (SHR)
- State
- PA Safe Schools Act (Title 30)
|
| |
| Reporting Issues |
- Incident
- Crime(s)
- Arrest(s)
- Charge(s)
|
| |
| Judgement Issues |
- Threshhold
- Punishment
- Prosecution
|
| |
| Outside Data |
| |
| Data Comparisons |
- Allegheny County
- Philadelphia County
- Potter County
- Pennsylvania
- Nation
|
| |
|
| Navigation: |
|
|
| |
|
| Copyright © 2011 - 2014 Ken Sochats |




































